What is Search Engine Marketing?

So, have you been considering marketing the products and/or services your business offers on the internet but not sure where to start? The fact is, that anyone with a product or service can benefit from search engine marketing. And the key to effective search engine marketing starts with solid keyword research, but more about that later!
According to Leeron Hoory, of www.forbes.com, “Search engine marketing (SEM) refers to the practice of improving how customers find your product or service on a search engine (such as Google or Bing) through paid advertising.” Now you may be wondering about organic marketing–where SEM used to refer to both paid and organic (unpaid) marketing, it is now attributed only to paid marketing.
Now That you know what SEM is… how is it different from SEO?
Since this is an article about SEM, it is important to address the difference between search engine optimization (SEO) and SEM. According to Hoory, “Search engine optimization (SEO) refers to optimizing website traffic from search engines to increase traffic organically.” On the other hand, SEM focuses on paid web advertising, often referred to as pay-per-click (PPC).
Why use Search Engine Marketing?
SEM is used regularly to attract the right customer at the right time. Without SEM, targeted customers might not easily find your product or service; this simplifies this process for them (and for you)!
This brings us to an excellent point: SEM is not an ‘aggressive’ marketing technique–you see, when a customer is searching based on their wants/needs, your product/service will simply show up in their search–there is no need for skeevy marketing techniques here!
Last, but not least, SEM only charges you when a customer clicks on your ad–thus, it is a cost-effective marketing strategy.
The Benefits of Search Engine Marketing
The benefits of SEM include, but are not limited to, the following:
- Marketing to the right person, at the right time: Targeting advertisements is a critical part of SEM. When a user searches for a solution, your ad can offer them a product or service that addresses their problem/need.
- Cost effective based on PPC: SEM is paid each time someone clicks on your ad – because these are targeted ads, the person most likely will have some sort of interest in your product or service.
- Quick and operative: The entire SEM process is fairly quick; thus it’s great for newer businesses to receive exposure. You could be on page one of Google in a matter of hours!
- ROI Measurable in real-time: With SEM, you are able to see when someone clicks your ad and when they buy something from you after clicking your ad; this allows you to make any necessary adjustments to your SEM ads.
How Does SEM Work?
Search engine marketing works by paying for advertisements to appear in search engines for particular searches. Each time a user clicks on the ad, the advertiser pays for the click, known as PPC or “pay-per-click”. Through the headline, description, extensions (which are optional), and the landing page, users will hopefully be converted into customers–it’s important to note that this requires adequate strategizing. Some things to consider include the following:
- Solid keyword research: just coming up with a few one-word keywords is not enough.
- Compare your current and prospective ads to your competitors’ ads: it’s important to see where you line up to your competitors. How can you get an edge over your competitors? What do you need to change to stay relevant?
Keywords, Keywords, Keywords!
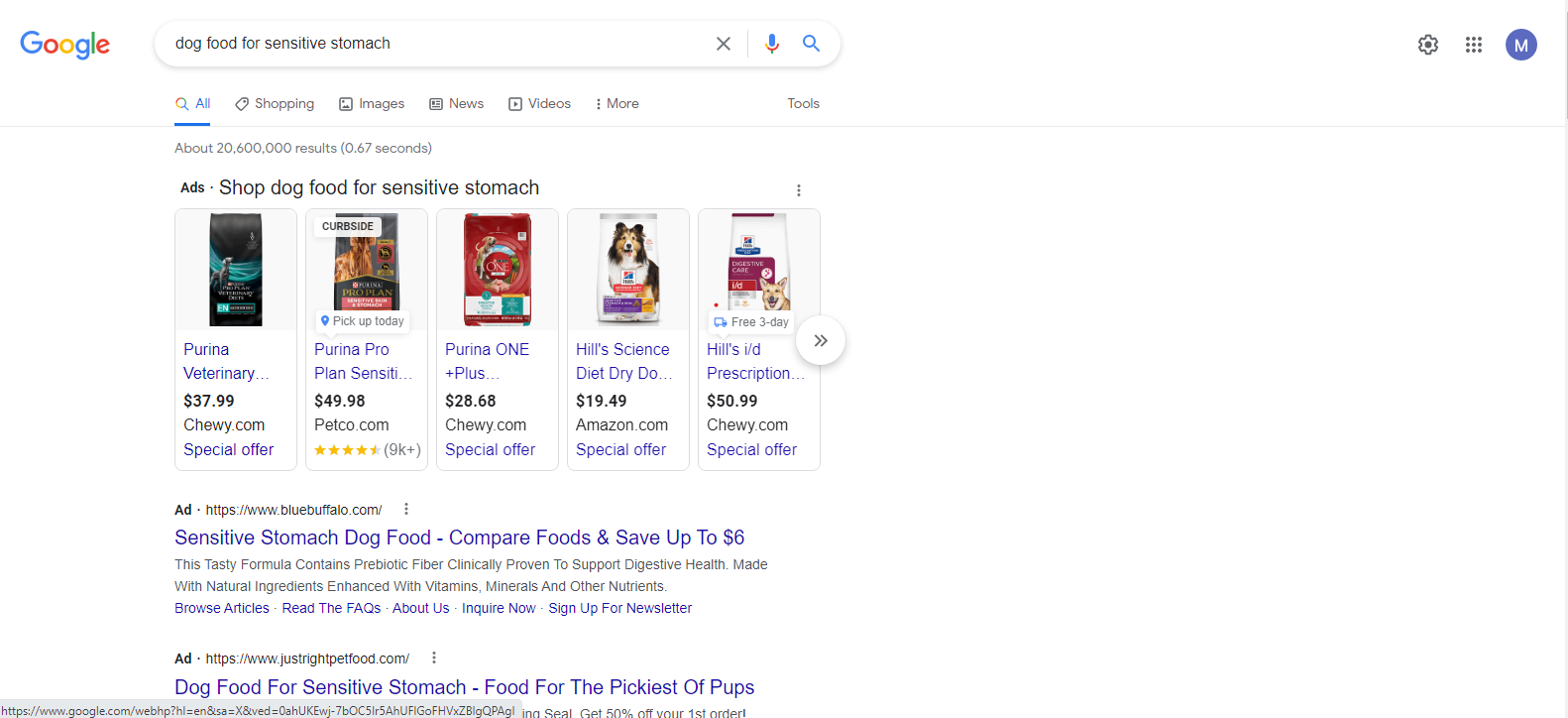
Much like SEO, keywords are imperative to success in SEM. This requires research; while keywords that reach your target audience are best, it’s also important to consider what keywords will reach the people who are ready to buy right now. Another important aspect is search intent–search intent allows for you (the marketer) to see things through the eyes of your prospective customers. For instance, if a customer wants to know what the average price of sensitive stomach dog food is, you can target your keywords to maximize the user experience.
Consider the example shown in the image below. The market for dog food is expansive; as are many things with such broad keyword terminology. In the below search, you can see that we’ve gotten a bit more specific: ‘dog food for sensitive stomachs’. This is considered a long-tail, informational keyword, where it is more than 3 words and is more specific.
Search Ad Features
Search ads each contain similar parts. Headlines, descriptions, and landing pages are crucial, where extensions are optional.
- Headline: featured at the top of each search ad; these are hyperlinks in the Google search results and they are between 30-35 characters maximum.
- Description: these appear after the headline, describing the ad succinctly (less than 90 characters).
- Extensions: these are optional and allow for links to alternate actions within each ad.
- Landing Page: this is where your customer will end up, upon clicking your link.
For further information on search engine marketing, contact us or check out SEM Rush